The term computer refers to an electronic device that can be programmed
to perform calculations. Calculators, alarm watches, and CD players all have
them. But when we hear "computer" we tend to think of a desktop computer.
A computer has 3 primary functions. The first function is to receive input from
the user. This can be done in many formats, from typing a command on the keyboard,
to clicking the mouse. After the computer has handled the user's input, it performs
the second function, called processing. In this step, the computer interprets the
user's input and decides what to do with it. After processing the input, the computer
must display its work, called output. This can be done through a monitor, a printer,
speakers, etc. A secondary function of a computer is storage. Storage involves
retaining data for later use. This stored data can then be exchanged by the processing
function. The flow chart below explains this process:
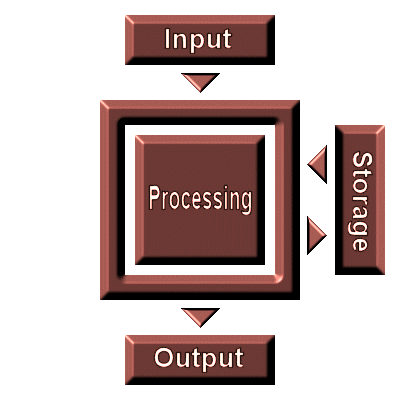
As you can see, the flow chart demonstrates that the input from the user is directed
to the processing function. The processing function interprets the input and turns
it into output. A secondary storage function also exchanges data with the processing
function. Every component of a computer pertains to one of these functions.