 |
| Motherboard |
 |
| |

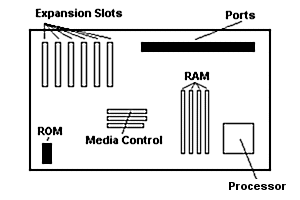
The motherboard is perhaps the most complex part of a computer because of all its
features. A computer's motherboard provides a platform for all of a computer's components
to mount. The motherboard also provides a connection between all of the parts attached
to it. There are 6 major areas of a motherboard:
• Processor
• RAM
• ROM
• Ports
• Expansion Slots
• Media Control |
 |
|
 |
 | |
The processor, also referred to as the central processing unit or microprocessor, is essentially
the "brain" of the computer. It performs complex mathematical operations based on sets of instructions.
Many processors today are so powerful that they require heat sinks and/or cooling fans.
|
|
 |
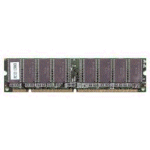 | |
RAM, short for Random Access Memory, is a set of integrated circuits that temporarily store
information that the computer can quickly refer to while the computer is turned on. Since
RAM storage is only temporary, the computer loses all information stored in RAM when the
computer is turned off.
|
|
 |
 | |
To learn about ROM, visit the BIOS section inside the Software page.
|
|
 |
 | |
Computers use ports to connect to external devices. There are several different styles of ports,
the most common are listed below:
• Parallel - This port transmits the bits of a byte over 8 different
wires simultaneously, one bit per wire.
• Serial - This port transmits the bits of a byte one after another over a single wire.
• USB - Short for Universal Serial Bus, this port can function as a keyboard, mouse, joystick, parallel,
or serial port. It is also fast enough to support video transfer.
• PS/2 - This port is a common hookup for keyboards or mice.
|
|
 |
 | |
Through the motherboard, a computer can have add-ons that enhance its performance and increase
its number of features. These cards slip into expansion slots on the motherboard. The most common
types of slots are listed below:
• AGP - Short for Advanced Graphics Port, this expansion slot was designed for 3D gaming,
and allows a direct link between the video card's graphics controller and the computer's main memory.
• ISA - ISA stands for Industry Standard Architecture. This older type of slot connects 8
or 16-bit cards to the bus.
• PCI - Short for Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI slots connect 32-bit cards to the
bus while operating faster than ISA slots.
|
|
 |
 | |
All drives, especially floppy drives and IDE devices (hard disks, CD-ROMs) use an I\O controller
to manage data transfer. For convenience, these controllers are placed on most of today's motherboards.
A common motherboard offers a connection to two floppy drives, and usually up to four IDE devices.
|
|
| |














